What is Acid Erosion?
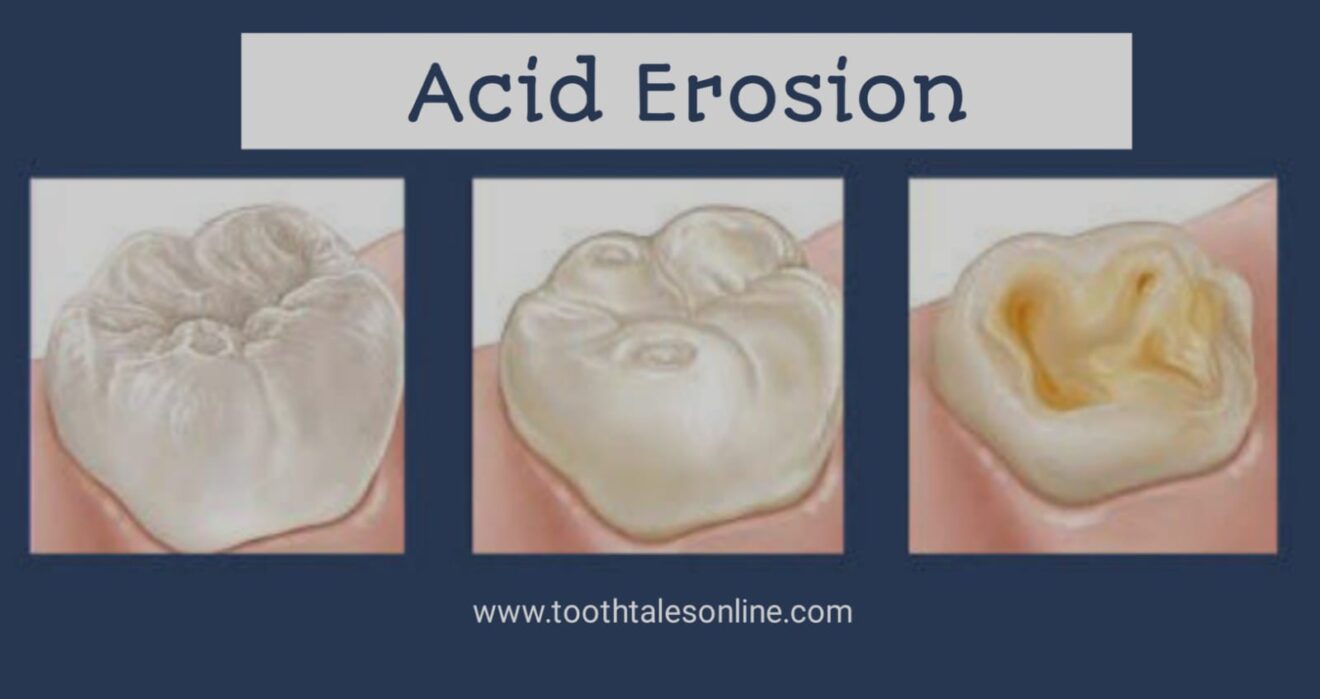
Acid erosion is a prevalent dental condition that occurs when acids wear away the enamel on teeth. Enamel is the protective outer layer of the teeth, and its erosion can lead to various dental problems. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, effects, and preventive measures for acid erosion.
Causes of Acid Erosion:
1.Dietary Factors:
Consuming a diet high in acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits and carbonated drinks, can contribute to acid erosion. Sugary snacks can also play a role in promoting acid formation.
2. Gastrointestinal Issues:
Individuals experiencing acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are at a higher risk of acid erosion. Stomach acid that enters the mouth can erode tooth enamel over time.
3. Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors, such as air pollution and acid rain, can indirectly contribute to acid erosion. Acidic substances in the environment can weaken teeth over time.
Effects of Acid Erosion:
1.Tooth Sensitivity:
Acid erosion can lead to the exposure of dentin, causing increased tooth sensitivity. Dentin is a softer tissue beneath the enamel that contains nerve endings.
2.Discoloration:
Eroded enamel may result in tooth discoloration, with teeth appearing yellow or discolored. This aesthetic concern can impact self-esteem and confidence.
3.Cavities and Decay:
As enamel erodes, the risk of developing cavities and dental caries increases. Enamel loss leaves teeth susceptible to decay and further damage. Acid erosion can alter the shape of teeth, leading to irregular edges and changes in overall tooth appearance.
Prevention and Treatment of Acid Erosion:
1.Dietary Modifications:
Adopting a balanced diet that includes low-acid foods and staying hydrated can help minimize acid erosion. Chewing sugar-free gum can also stimulate saliva production, which aids in neutralizing acids.
2.Proper Oral Hygiene:
Maintaining proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing with fluoride toothpaste, can strengthen enamel and reduce the risk of acid erosion.
3.Regular Dental Check-ups:
Routine dental check-ups enable early detection of acid erosion and other dental issues. Professional cleaning can help remove plaque and prevent further enamel damage.
4.Fluoride Treatments:
Dentists may recommend fluoride treatments, such as fluoride varnish or supplements, to strengthen enamel and protect against acid erosion.
5.Behavioral Changes:
Quitting smoking and avoiding acidic habits, such as excessive consumption of acidic beverages or frequent snacking, can significantly reduce the risk of acid erosion.
Short Review:
Understanding acid erosion is crucial for maintaining good oral health. By recognizing the causes, effects, and preventive strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their teeth from the damaging effects of acid erosion. Adopting a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, proper oral hygiene, and regular dental check-ups is key to preserving enamel and ensuring a healthy, confident smile.
FAQs:

















Add Comment