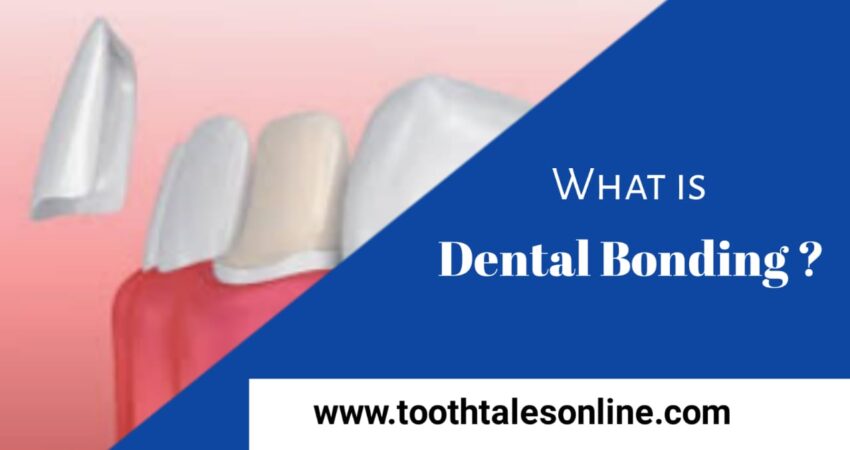
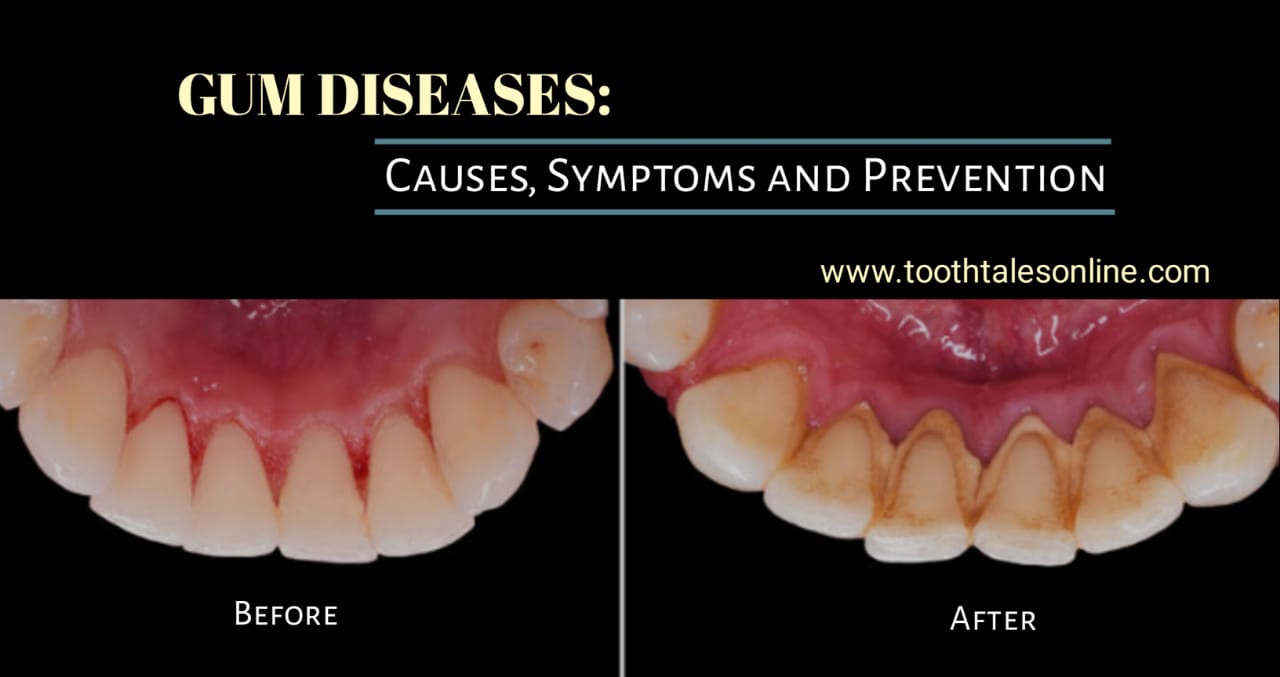
Gum Disease:
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is a common problem that affects the gums and the tissues around your teeth. It can get worse over time if not treated and may cause serious dental issues. Let’s talk about its causes, symptoms, and how you can prevent it.
What Causes Gum Disease?
1.Poor Oral Hygiene:
Not cleaning your teeth well is the main cause of gum disease. When plaque—a sticky layer of bacteria—builds up on your teeth, it irritates your gums. This can lead to gum inflammation.
2.Tobacco Use:
Smoking or using tobacco products makes gum disease worse. Nicotine reduces blood flow to your gums, making it harder for them to stay healthy and fight infections.
3.Genetics:
Some people are more likely to get gum disease because of their family history. If your parents or siblings had gum problems, you may be at a higher risk.
4.Poor Nutrition:
A diet missing important nutrients weakens your immune system. This makes it harder for your body to fight gum infections.
5.Health Conditions:
Diseases like diabetes and autoimmune disorders increase the risk of gum disease. Certain medicines that cause dry mouth can also lead to gum problems.
Symptoms of Gum Disease:
1.Bleeding Gums:
Gums that bleed when you brush or floss could be a sign of gum disease. Healthy gums shouldn’t bleed often.
2.Swollen or Tender Gums:
If your gums look red, feel swollen, or hurt to touch, it might mean they are inflamed.
3.Bad Breath:
Bacteria in plaque release toxins that can cause bad breath, even if you clean your mouth regularly.
4.Receding Gums:
When gums pull away from your teeth, it leaves pockets where bacteria can collect. This is a sign of worsening gum disease.
5.Loose or Shifting Teeth:
Severe gum disease can damage the structures that hold your teeth in place, making them loose or misaligned.
How to Prevent Gum Disease?
1.Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque. Using an antibacterial mouthwash can also help protect your gums.
2.Visit the Dentist Regularly:
Go for dental check-ups and cleanings every six months. Dentists can catch gum disease early and treat it before it worsens.
3.Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
Stop smoking, eat a balanced diet, and manage medical conditions like diabetes to keep your gums healthy.
4.Reduce Stress:
Long-term stress can weaken your immune system. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation to stay healthy.
FAQs:
1. What is gum disease, and how does it start?
Gum disease is an infection of the gums caused by plaque buildup. It usually starts with red, swollen gums that bleed easily.
2. Can gum disease be cured?
Early gum disease, called gingivitis, can be reversed with good oral care. Advanced stages may need professional treatment to manage.
3. What are the warning signs of gum disease?
Common signs include bleeding gums, bad breath, swollen gums, receding gums, and loose teeth.
4. How can I prevent gum disease at home?
Brush and floss every day, use an antibacterial mouthwash, and eat a healthy diet. Regular dental visits are also essential.
5. Does gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, untreated gum disease has been linked to other health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues.
6. Can kids get gum disease?
Yes, children can get gum disease, especially if they don’t brush and floss regularly.
7. Does smoking make gum disease worse?
Absolutely. Smoking weakens the gums’ ability to heal and fight infections, making gum disease harder to treat.
8. What treatments are available for gum disease?
Treatments include deep cleaning (scaling and root planning, antibiotics, and sometimes surgery for severe cases.
















Add Comment