Sensitivity is a common and often misunderstood phenomenon that can affect various aspects of our lives, from interpersonal relationships to physical well-being. In this article, we will delve into the concept of sensitivity, exploring its definition, causes, and effective strategies for prevention.
What is Sensitivity?
Sensitivity, in a broad sense, refers to the heightened responsiveness of an individual to stimuli, whether they are emotional, physical, or environmental. People may experience sensitivity in various forms, including emotional sensitivity, sensory sensitivity, and even dental sensitivity. Understanding the root causes of sensitivity can empower individuals to take proactive measures to manage and prevent its negative impact.
Causes of Sensitivity:
- Biological Factors:
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may inherit a higher sensitivity threshold from their parents, making them more prone to heightened reactions.
- Neurological factors: Variations in brain chemistry and function can contribute to increased sensitivity in certain individuals.
- Environmental Factors:
- Overstimulation: Exposure to excessive stimuli, such as loud noises, bright lights, or crowded spaces, can trigger sensitivity in some people.
- Allergens: Environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust, or pet dander, can lead to heightened sensitivity in individuals with allergies.
- Psychological Factors:
- Past trauma: Individuals who have experienced trauma may develop heightened emotional sensitivity as a coping mechanism.
- Anxiety and stress: High levels of stress and anxiety can amplify sensitivity, both emotionally and physically.
- Health Conditions:
- Chronic illnesses: Certain medical conditions, such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome, can contribute to increased sensitivity.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormonal levels, particularly during pregnancy or menopause, can result in heightened sensitivity.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
- Mindfulness Practices:
- Meditation and deep breathing exercises can help individuals become more aware of their reactions to stimuli, allowing them to respond in a calmer manner.
- Environmental Modifications:
- Creating a comfortable and quiet space can minimize overstimulation, particularly for those sensitive to external factors.
- Using air purifiers and maintaining a clean living environment can reduce exposure to allergens.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Regular exercise has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, potentially mitigating sensitivity.
- Adequate sleep is crucial for overall well-being and can positively impact emotional and physical sensitivity.
- Therapeutic Interventions:
- Seeking therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals address underlying psychological factors contributing to sensitivity.
- Occupational therapy may provide practical strategies for managing sensory sensitivity.
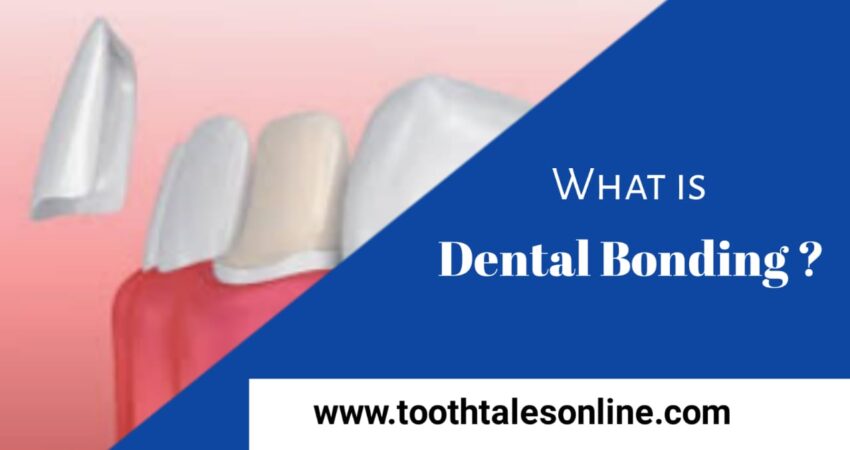
- Dental Sensitivity Prevention:
- Using desensitizing toothpaste and maintaining good oral hygiene practices can alleviate dental sensitivity.
- Regular dental check-ups can identify and address underlying issues causing sensitivity.
Sensitivity is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human experience, influenced by a combination of biological, environmental, and psychological factors. By understanding the causes of sensitivity and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and lead more fulfilling lives. Whether it’s emotional, sensory, or dental sensitivity, a proactive and holistic approach can make a significant difference in managing and minimizing the impact of sensitivity on one’s life.



















Add Comment